As students, we often find ourselves spending most of our time, on our desks at school or our study table at home.
Studies show that the quality of these facilities directly impacts our performance and that our physical environment affects the way we receive and process information, and our satisfaction towards educational facilities increases our skills and cognitive abilities.
Most of a student’s life involves sitting on a chair for long hours; hence, this piece of furniture has become a pivotal element towards providing a comfortable and efficient educational environment for a student.
The Effects of Sitting for Long Hours
Sitting on conventional chairs for prolonged periods may have its long term physical and behavioral consequences, as these chairs tend to introduce poor sitting positions and bad posture.
Tasks that involve prolonged sitting, such as studying or working on a computer, are identified as risk factors in contributing to lower back pain, especially when using poorly-designed seats.
Effects on Cognitive and Academic Performance
In a study conducted by M. Kashif, et. al., (2015), several physical factors brought about by sitting on conventional school chairs were determined to contribute to bad posture, which eventually lead to muscle fatigue, diminished academic performance and productivity, and in some cases, injury.
Other studies have also looked into the correlation of bad posture and cognitive abilities such as reaction time, consciousness and discomfort.
Effects on Physical Health
In terms of physical health, using conventional chairs for prolonged periods can cause a number of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), particularly on the waist, neck, and shoulder areas.
Additionally, a sedentary posture can limit the nutritional intake of the spinal disks, causing them to be less flexible over time. Blood flow is also reduced towards the lower extremities, leading to muscle tension and weakness in the lumbar-pelvic region.
Factors that Determine the Ergonomic Quality of Chairs
N. Al-Hinai et. al., (2018) and M. Kashif, et. al., (2015) identified key factors that impact the ergonomic quality of chairs and desks for educational use.
The dimensions of these factors should fit well with the measurements of the human body. A mismatch between a chair’s dimensions and the anthropometric data (body measurements) of the user can be the cause of physical strain, as well as restlessness and lack of concentration.
Some of the factors that are essential in the design of an ergonomic chair include the following:
- Seat height – The distance of the seat from the ground, with basis on a person’s knee (popliteal) height
- Seat length and width – Support hip breadth and anthropometric length between the buttocks and the back of the knee
- Seat depth – Provides ample support on the curve of the buttocks while seated
- Backrest shape and angle – Ensure support on the lower back (lumbar region) and encourages a variety of movements while seated
Types of Chairs Suitable for Studying
Seated tasks such as studying can be performed on a wide range of positions – reclined, upright, declined, and standing. Hence, ergonomic chairs are typically designed to have adjustable features to accommodate various sitting positions.
Some ergonomic chairs are also designed to specifically cater to a single sitting position, but with added features to provide the user mobility and flexibility while performing seated tasks. The following are some types of ergonomic chairs that are suitable for studying:
1. Standard Office Chair

A standard office chair may come in different forms and features, but it is essentially the traditional chair that we are all used to.
The standard office chair promotes a trunk-to-thigh sitting angle of 90 degrees, and some research studies have shown that the typical sitting posture can lead to lower back pain due to the increase in pressure on the spinal discs (Gale, M., et al., 1989).
Nevertheless, a standard office chair is an economic option in providing relief and comfort in performing seated tasks such as studying.
2. Kneeling Chair
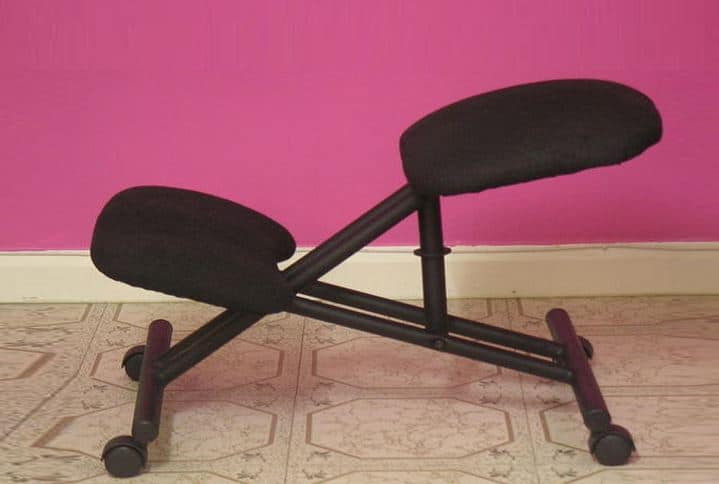

A kneeling chair supports a declined sitting position, wherein the main seat is sloped at a downward angle of 20 to 30 degrees such that the knees are pointed downwards. Cushioned pads are in place to support the shins and to keep the body from falling forward.
This open angle between the torso and the knees reduces strain from the back and strengthens the core muscles. In a study conducted by Vaucher, M., et al. (2015), it was observed that kneeling chairs helped to reduce lumbar lordosis among patients suffering from lower back pain.
In contrast, participants of Colin Drury and M. Francher’s study complained of leg discomfort while using the kneeling chairs over an extended period.
3. Saddle Chair
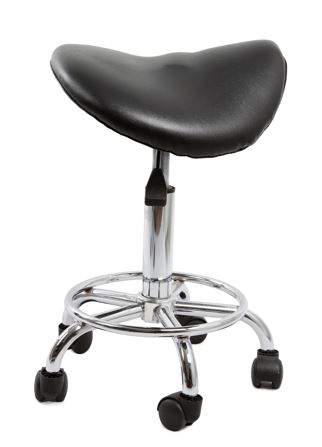
A saddle chair takes its name from a horse’s saddle, because it supports a declined sitting position similar to riding a horse. A saddle chair contours the thighs to a 135-degree slope to support the lumbar curve.
A solid seat design features a seat similar to a conventional stool, while a divided seat has two cushions parted at an angle mirroring the shape of the legs. Compared to conventional chairs, saddle chairs reduce lower back pain and discomfort.
However, prolonged sitting on saddle chairs can cause discomfort on the lower limbs, as well as the buttocks and hips (Gadge, K., et al. 2007).
4. Exercise Ball Chair

An exercise ball chair is essentially a rubberized inflated yoga ball placed on a circular base or covered in anti-slip material to keep it from rolling. Exercise ball chairs have become a popular alternative to conventional chairs, as it provides more flexibility while performing seated tasks.
The use of an exercise ball chair has proven to help people with desk jobs burn more calories – around 4 per hour – compared to when sitting on traditional office chairs (Beers, E.A., et al., 2008).
However, a New York Times wellness article in 2013 cited that a research conducted by Jack A. Callaghan, the Canada Research Chair in Spine Biomechanics and Injury Prevention at the University of Waterloo, Ontario, revealed that sitting on an exercise ball chair may contribute to a slumped sitting position, as the increase in the contact area between the buttocks and the chair’s surface causes the person to sink into an exercise ball chair.
5. Recliner Chair
As suggested by its name, a recliner chair supports a semi- to fully-reclined sitting position. This type of chair allows an adjustable backrest angle to diminish stress on the back; however, there’s no way to pair this up with a traditionally-designed desk.
Seated tasks may be performed on a reclining chair by attaching a specialized desk onto the chair. Research has shown that the optimum sitting position is an open angle of 135 degrees between the thighs and the trunk (Bashir, W. A., et al., 2007).
Sitting on a reclined position is anatomically sound, as this alleviates stress on the spine and reduces the risks for back pain.
6. Tablet Armchairs
Tablet armchairs are the ergonomic version of the traditional school armchairs with built-in desk surfaces for writing. It features an adjustable tablet attached to the armrests, and the seats are cushioned and covered in leather or fabric.
Modern tablet armchairs designed to offer great mobility were found to be one of the best choices of furniture among students, as the added mobility likely engages changes in posture through physical movement; thus promoting active sitting (Harvey, E. & Kenyon, M., 2013).
7. Cane or Stick Chair
Stick chairs take ergonomics to whole new level by featuring a stool-like seat that is supported by only one leg, which is padded with a rubber grip to stay in place on almost any surface.
A stick chair supports a declined sitting position, and using one is just like standing, except that it supports some of the body’s weight.
Stick chairs are relatively new in the ergonomics department; hence, studies are yet to be conducted to gauge their effectivity in taking off the pressure on the legs and the lower back.
8. Active Sitting Chair
An active sitting chair may look like a traditional office chair at first glance, but it is designed to have an unstable base to help promote movements and flexibility while seated. The cushioned seats and backrests are often covered with a breathable mesh cloth for added comfort.
Researchers from the Cornell University in New York concluded that active sitting chairs may counteract the health hazards of static sitting, as these were found to be more comfortable.
However, performance of computer tasks was the same as when seated on a conventional office chair.
9. Leaning Sit Stand Chair
A leaning sit stand chair is commonly paired with a standing desk, and it offers easy transition between standing and sitting positions.
A leaning sit stand chair supports a declined sitting position, wherein the thighs are angled downward. It often comes with foot pads that provide comfort and alleviate soreness on the joints.
A leaning sit stand chair promotes active sitting and is found to correlate with improved job performance and reduced occupational fatigue (Edwardson, C., et al., 2018).
However, field studies from Cornell University showed that the combination of a leaning sit-stand chair and a standing desk, as a workstation, only contributes to 15 minutes of standing activity among users.
Additionally, computer users with a sit-stand workstation were found to be at risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders on the wrist due to poor wrist posture.